Bluetooth is a wireless technology that allows mobile and stationary devices to exchange data over short distances, “Definition of Bluetooth” enabling the creation of personal area networks.
Class and supported profiles are the two key characteristics of Bluetooth devices.
The term “Class” describes the range at which Bluetooth connectivity is achievable. Since most mobile devices are Class 2, they can go up to 10 metres. Rare and having a range of up to 100 feet are class 1 devices in Bluetooth.
One kind of Bluetooth connection is called a “profile”. The most popular profiles that allow the device to connect to a wireless headset or handsfree are Headset (HSP) and Handsfree (HFP).
Other features in Bluetooth include AVRC, which enables playback control remotely, A2DP, which provides support for stereo sound streaming, and OBEX (OBject EXchange), which facilitates the transmission of files, contacts, and events. And more about features of Bluetooth is given below.

Table of Contents
ToggleBluetooth features include:
- specifications using spread spectrum technology with frequency hopping.
Up to seven devices can build a network and connect with a master Bluetooth device.
Using a Netgraph framework and short wavelength radio communication signals, the FreeBSD stack is operated.
- Device technology uses Secure and Fast Encryption Routine (SAFER)+ block cypher algorithms for authentication, secrecy, and key generation.
Several different uses of Bluetooth connections:
- Mobile devices and hands-free headsets may communicate and operate wirelessly.
- Multiple PCs connected via wireless networking in places with spotty service
PCs and peripheral input/output (I/O) devices wireless communication
- Object Exchange (OBEX) allows calendar appointments, contact information, and files to be shared across several devices.
- can take the role of traditional cable communication devices such as bar code scanners, GPS receivers, medical equipment, and traffic control systems
- When a larger USB bandwidth is not required for low-bandwidth applications
- Connect many industrial Ethernet networks together
- Numerous interactive games and play stations come with wireless controllers.
- Use a PC or PDA to access a dial-up Internet connection.
- Oversee the short-range data transfer between cellular and other telehealth devices and medical equipment.
- Digital enhanced cordless telephony (DECT) for mobile phone communication
Use the real-time location system to locate and monitor objects.
- Monitor the movement of prisoners and livestock.
- Applications for personal mobile security
For short-range data transmission between stationary and mobile electronic devices, Bluetooth is an open wireless technology standard. In 1994, Bluetooth was unveiled as a wireless alternative to RS-232 wires.
In the unlicensed 2.4 GHz band, Bluetooth establishes personal networks and connects with a wide range of electrical gadgets. Operating range varies according to gadget type. Bluetooth is a technology used by many digital devices, such as MP3 players, laptops, mobile phones, and peripherals.
Unlike previous wireless technologies, Bluetooth offers high-level services including voice transmission, file pushing, and serial line emulation on its network and devices.
The Scandinavian phrase Blåtand/Blåtann, which was first used by Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson I, a native of Denmark and a portion of Norway, is whence the name Bluetooth originates. As a monarch, he brought the warring Danish tribes together to form a unified kingdom during the tenth century. The name Bluetooth was created to signify the unification of many communication technologies into a single, global standard.
For why is Bluetooth used for?
Early iterations of Bluetooth made it possible for owners of cell phones, pagers, and PDAs to purchase a three-in-one phone that could be used for portable phone use at home or at work, quickly synchronise with data on a desktop or notebook computer, start a fax machine or send one, start a printout, and, generally, have all mobile and fixed computer devices completely coordinated over a short distance.
More latest Bluetooth versions allow users to link wireless headphones to a smartphone’s music library or make hands-free phone calls using a mobile device. Using Bluetooth technology, tasks that once required several cables scattered across various peripheral devices may be made simpler. For example, printing documents wirelessly from a desktop, laptop, or mobile device is possible with a printer that supports Bluetooth. A wireless keyboard may also be synced with a tablet device, such a Kindle Fire or an Apple iPad, or even a DVD player with a TV.
Furthermore, users of mobile operating systems may use Bluetooth to stream media—including music, movies, and TV shows—to TVs, speakers, and media players that are compatible. Companies like LG are producing televisions with integrated Bluetooth technology that can show 3D pictures that viewers watch through special “active-shutter” glasses, with an eye towards the future of the technology. Even though this technology is still in its early phases, gamers have responded quite positively to it.
Without integrated Bluetooth, desktop or laptop PCs can acquire such features via a cheap USB dongle. The one thing to keep in mind is that Bluetooth technology often consumes a significant amount of battery life; therefore, it is advised that users regularly check it to avoid a device’s battery dying.
How does Bluetooth work properly?
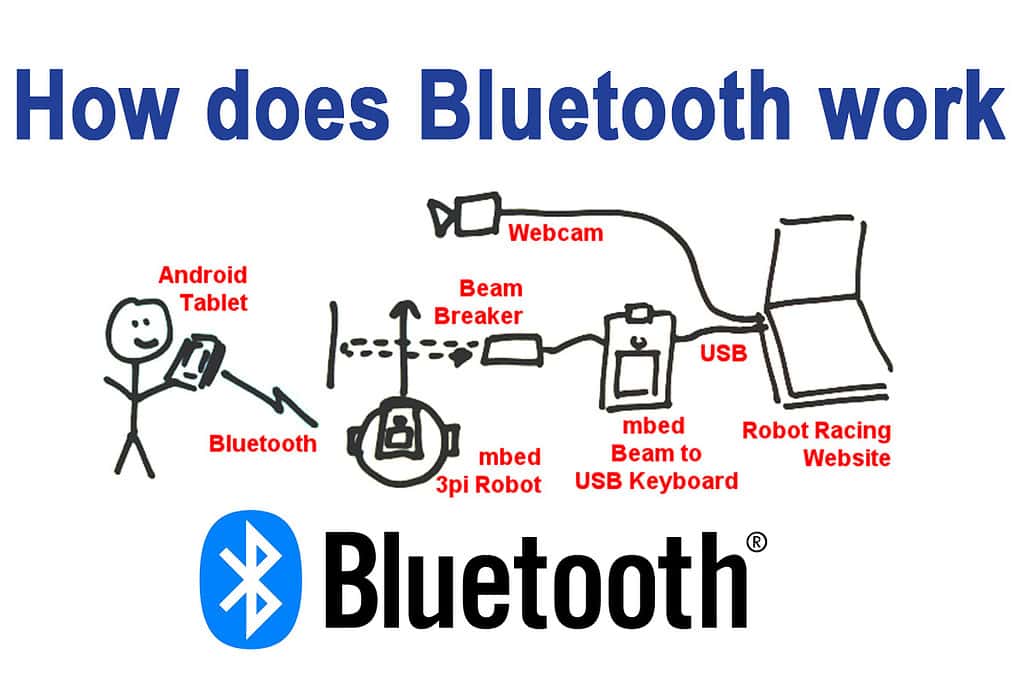
For Bluetooth to work, every gadget has to have a cheap transceiver chip. The transceiver operates in a 2.45 GHz frequency spectrum that was previously unoccupied and is accessible worldwide, however bandwidth varies slightly throughout nations. There are up to three voice channels accessible in addition to data. The IEEE 802 standard provides a unique 48-bit address for every device. Point-to-point and multipoint Bluetooth communications are both possible.
Ten metres is the maximum Bluetooth range. One megabit per second (Mbps) of data interchange is possible, with the potential to reach two Mbps with the next generation of technology. Devices can interact even in locations with high levels of electromagnetic interference thanks to frequency hop schemes. There is encryption and verification built right in.
How Bluetooth Works
Pairing is the procedure by which two Bluetooth devices are connected to one another. A Bluetooth device starts a new connection when you push a button or choose an item from the menu. Depending on the device type, different details apply.
Bluetooth radios are built into a lot of mobile gadgets. Bluetooth dongles can also be used to enable PCs and other devices.
A piconet, a dynamic architecture seen in Bluetooth networks, is composed of two Bluetooth peer devices at minimum and up to eight at most. Network protocols included in the Bluetooth standard are used by devices to connect with one another. Over the years, the Bluetooth standards have undergone revisions. Version 1.0, which is not commonly used, was followed by versions 1.1 through 5.
Up to the most recent standard, Bluetooth-transmitted radio signals could travel only a small distance—typically up to 30 feet. Although Bluetooth’s performance has significantly improved over time due to technological developments, it was initially intended for slower wireless communications. Modern implementations of the standard are rated up to 50 Mbps, although earlier versions permitted connections as little as 1 Mbps.
Security about Bluetooth
Bluetooth has been under fire over the years for network security flaws, just like other wireless technologies. In popular TV dramas, crooks are occasionally seen linking their Bluetooth phone with an unsuspecting victim’s so they may steal sensitive information and eavesdrop on conversations. Naturally, these assaults are quite unlikely to occur in real life and occasionally aren’t even conceivable in the manner that they are shown.
Even though Bluetooth technology has several security safeguards, security experts advise shutting off Bluetooth while a device is not in use to reduce any potential risks.
Use of Bluetooth
Although Bluetooth compatibility is present in many different devices, its primary purpose was to facilitate the networking of battery-operated portable consumer electronics and accessories. Examples of such products include:
- Mobile phones
- wireless headphones, such as kits for hands-free driving
- Keyboards that are wireless
- Printers
- Speakers that are wireless
- Computers
FAQ'S
What are some common Bluetooth use cases?
To think about transmitting energy up to five centimetres to charge several gadgets.
How does Bluetooth pairing work?
If two devices are paired with Bluetooth, they can establish a connection and save each other’s pairing details on Bluetooth.
What is the Simple Definition of Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is a method for date communication that uses short-range radio links to replace cables Between computers and their connected unite. For more Definition of Bluetooth read more.
What is the Simple Definition of Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is a method for date communication that uses short-range radio links to replace cables Between computers and their connected unite. For more Definition of Bluetooth read more.




Good explination